Unremarkable controls, exciting design, and an original idea help users understand the concept, purpose, and mechanics of the hyper-casual game. The method of the levels is another part of the puzzle. Suren Melkonyan, game designer at Supersonic, shares three tips that will attract users and increase retention.
Environment and level animation
Environment and animation work together to support the concept of the game. These parameters are related to each other at each level. For example, in Going Balls, there are two levels with environments, one city and one forest.

The city level depicts buildings and streets immediately recognizable as urban elements. The colour contrasts with the track, so the gameplay remains clear but immerses users in the theme of the level, thanks to the design in the background. The forest level shows a background with green trees and a blue river that refers to the natural environment. These two levels include an art design that feels intuitive.
Level structuring depends on the genre of the game
User behaviour changes depending on the genre of the game. For example, ASMR games are played to relax, while puzzle games are played to realize themselves by solving complex problems. The design of levels takes into account the psychology of users. Anticipating user behaviour will help create levels that satisfy players’ needs and increase retention.
Side note: How to lower CPI after launch and improve profitability with creatives
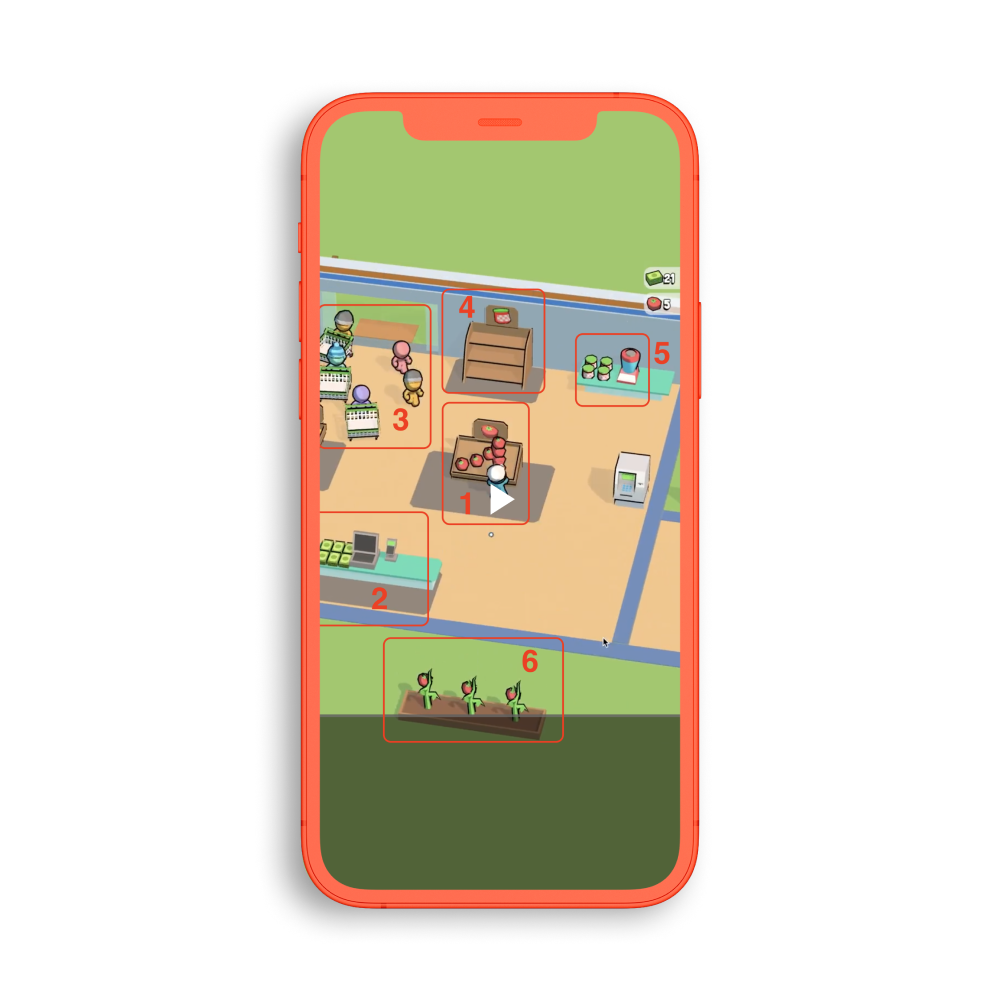
In arcade games, users experience a sense of development as they gather resources, spend them on upgrades, and continue the cycle to build a mini-market, farm, restaurant, etc.

Design optimization
Level dropout is a metric that is analyzed to improve the design of hyper-casual game levels. Developers are shown the percentage of users who do not pass a level, allowing them to determine at what point in the game users drop out.
Often users don’t understand how to play a level or its purpose, which leads to a higher dropout rate. These problems are solved by creating learning levels. The first learning level contains an index showing users how to operate the game and the goal. The second highlights a specific feature. For example, a gate with a multiplier so users know what to do to pass the level. Both tutorials help achieve the main goal: to keep users in the game.
Conclusion
Hyper-casual games are easy to understand, from learning to art design. Users play for 2-3 minutes. During this time, it is necessary to attract attention, explain the rules, and make sure that the game’s goal is known. Improving the level design, intuitive gameplay, and meeting user expectations increases gamer engagement.

1,306












 3 minutes
3 minutes








 2 minutes
2 minutes
